Ear, Nose, and Throat: A Trio of Troublemakers
The ear, nose, and throat are a trifecta of interconnected structures that play vital roles in our sense of hearing, smell, taste, and communication. Unfortunately, these interconnected systems are also susceptible to a variety of problems that can cause discomfort, disrupt daily activities, and sometimes signal underlying health conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into common ear, nose, and throat (ENT) problems, their causes, treatment options, and preventative measures.
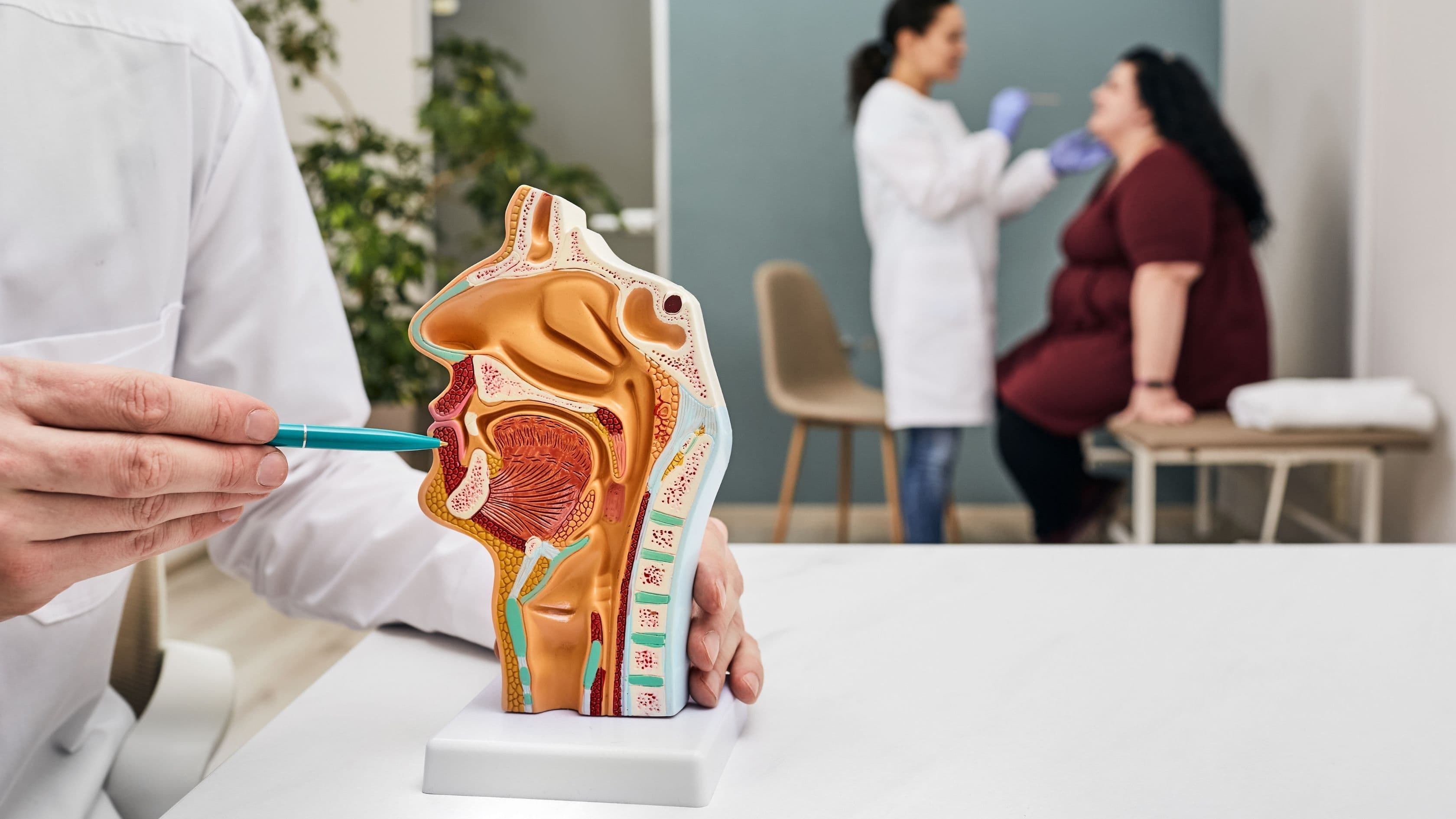
Understanding the ENT System
- The Ear:
- Responsible for hearing and balance.
- Composed of three main parts: the outer ear (funnel-shaped part we see), middle ear (contains the eardrum and tiny bones), and inner ear (responsible for balance and hearing perception).
- The Nose:
- Serves as the primary organ of smell and the gateway to the respiratory system.
- Lined with a mucous membrane that traps dust, allergens, and other irritants.
- Plays a role in regulating temperature and humidity of inhaled air.
- The Throat:
- Connects the mouth and nose to the airway and esophagus.
- Essential for breathing, swallowing, and speech.
- Contains tonsils and lymph nodes that help fight infection.
The Interconnected Web:
The ENT system is intricately linked. The Eustachian tube, for example, connects the middle ear to the back of the nose, allowing pressure equalization and drainage of mucus. Similarly, the tonsils and adenoids located in the throat are part of the immune system and can impact the nose and sinuses.
A Spectrum of Symptoms:
ENT problems can manifest through a variety of symptoms, including:
- Ear: Pain, fullness, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), vertigo (spinning sensation), drainage.
- Nose: Runny or stuffy nose, congestion, sneezing, loss of smell, facial pain, sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses).
- Throat: Sore throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, tonsillitis, allergies.
Common ENT Problems:
- Ear Infections: Bacterial or viral infections, especially common in children, causing ear pain, fever, and drainage.
- Swimmer's Ear: Inflammation of the outer ear canal, often due to water exposure, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Hearing Loss: Can be temporary or permanent, caused by various factors like age, noise exposure, earwax buildup, or ear infections.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses, resulting in facial pain, congestion, and headaches.
- Allergies: Seasonal allergies or allergies to dust, mold, or pet dander can cause a runny nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes.
- Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils, causing sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and fever.
- Strep Throat: Bacterial infection of the throat, presenting with a severe sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the voice box, causing hoarseness, loss of voice, and a scratchy throat.
Consulting an ENT Specialist:
For persistent or severe ENT problems, consulting an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) is recommended. ENT specialists have the expertise to diagnose and treat a wide range of ear, nose, and throat conditions.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and potentially other tests like allergy testing, hearing tests, or imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans) depending on the suspected issue.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for ENT problems varies depending on the specific diagnosis. Here are some common approaches:
- Medications: Antibiotics for infections, allergy medications, decongestants, pain relievers, or topical steroids depending on the condition.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Earwax removal, nasal irrigation, or allergy shots.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary, such as tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis or surgery to correct a deviated septum (misaligned nasal bone).