Unveiling the Heart's Secrets: A Comprehensive Guide to Echocardiography
The human heart is a remarkable organ, tirelessly pumping blood throughout the body to sustain life. Echocardiography, also known as an echo or heart ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging technique that offers a window into the heart's inner workings. This informative guide delves into the intricacies of echocardiography, explaining its purposes, procedures, benefits, and limitations.
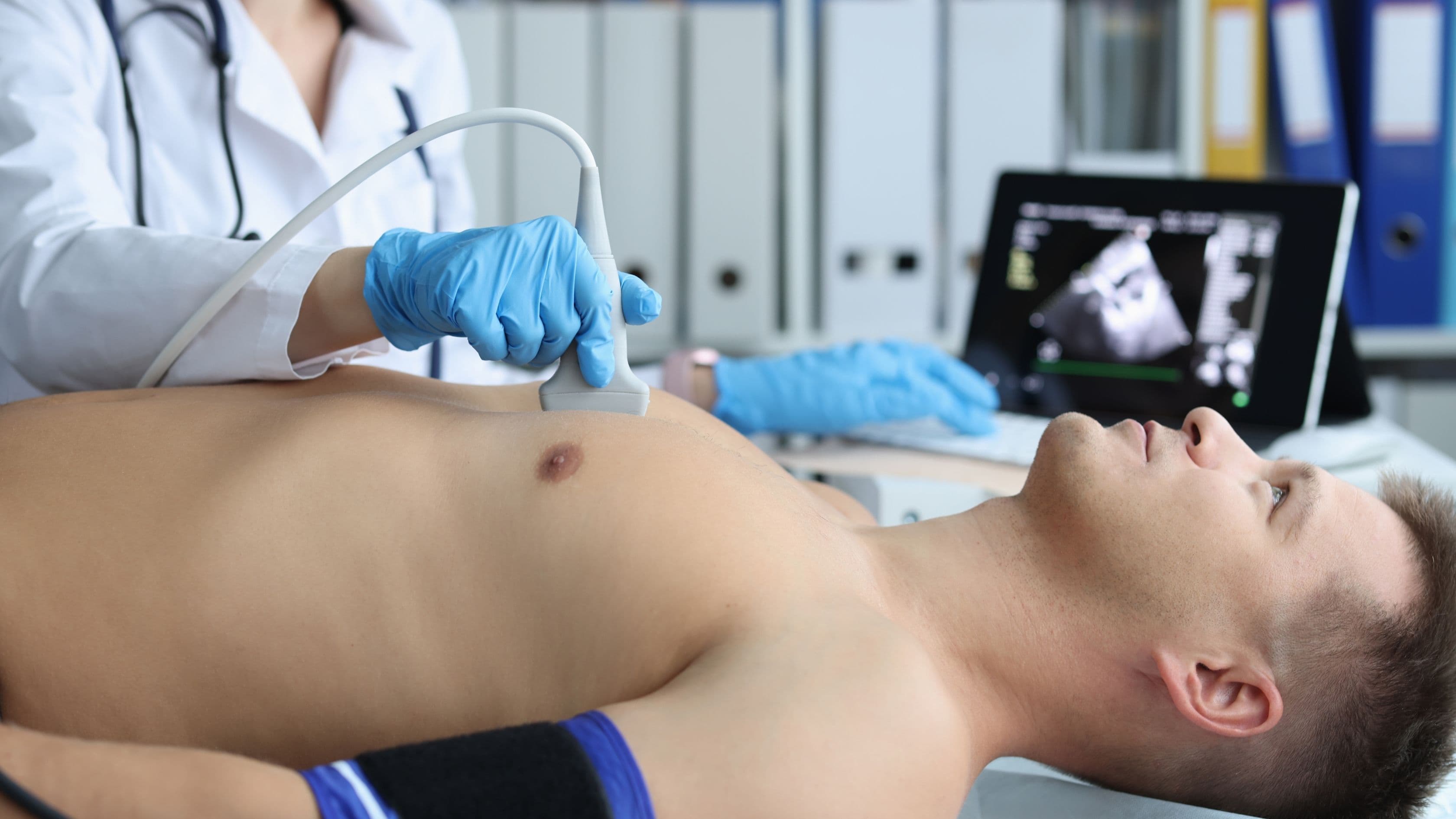
What is Echocardiography?
Echocardiography utilizes high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to generate detailed images of the heart. Unlike traditional X-rays, which capture still images of bones, echocardiography provides real-time moving pictures of your heart's structures and blood flow. This allows doctors to assess the heart's:
- Size and shape: Identify any enlargements or abnormalities in the heart chambers.
- Wall movement: Evaluate the pumping strength and efficiency of the heart muscle.
- Valve function: Assess whether the heart valves are opening and closing properly to ensure efficient blood flow.
- Blood flow patterns: Visualize blood flow through the heart chambers and valves, identifying any blockages or abnormal flow patterns.
The Two Main Types of Echocardiograms:
There are two main types of echocardiograms, each offering unique perspectives of the heart:
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): This is the most common type of echo. A transducer (probe) is placed on your chest wall to transmit sound waves through your chest tissues and capture images of your heart.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): For a more detailed view, a TEE uses a thin probe inserted through your esophagus (the tube connecting your mouth to your stomach) to get closer images of the heart, particularly the rear structures.
Echocardiography is a safe and painless procedure that provides valuable insights into the heart's function. It is a versatile tool used for various diagnostic purposes.