World Hepatitis Day 2024: Understanding, Preventing, and Fighting Hepatitis
Every year on July 28th, the world comes together to raise awareness about hepatitis and the urgent need to prevent, diagnose, and treat this silent epidemic. World Hepatitis Day 2024 shines a spotlight on a global health issue that affects millions, yet remains under-discussed and often misunderstood.
What is Hepatitis?
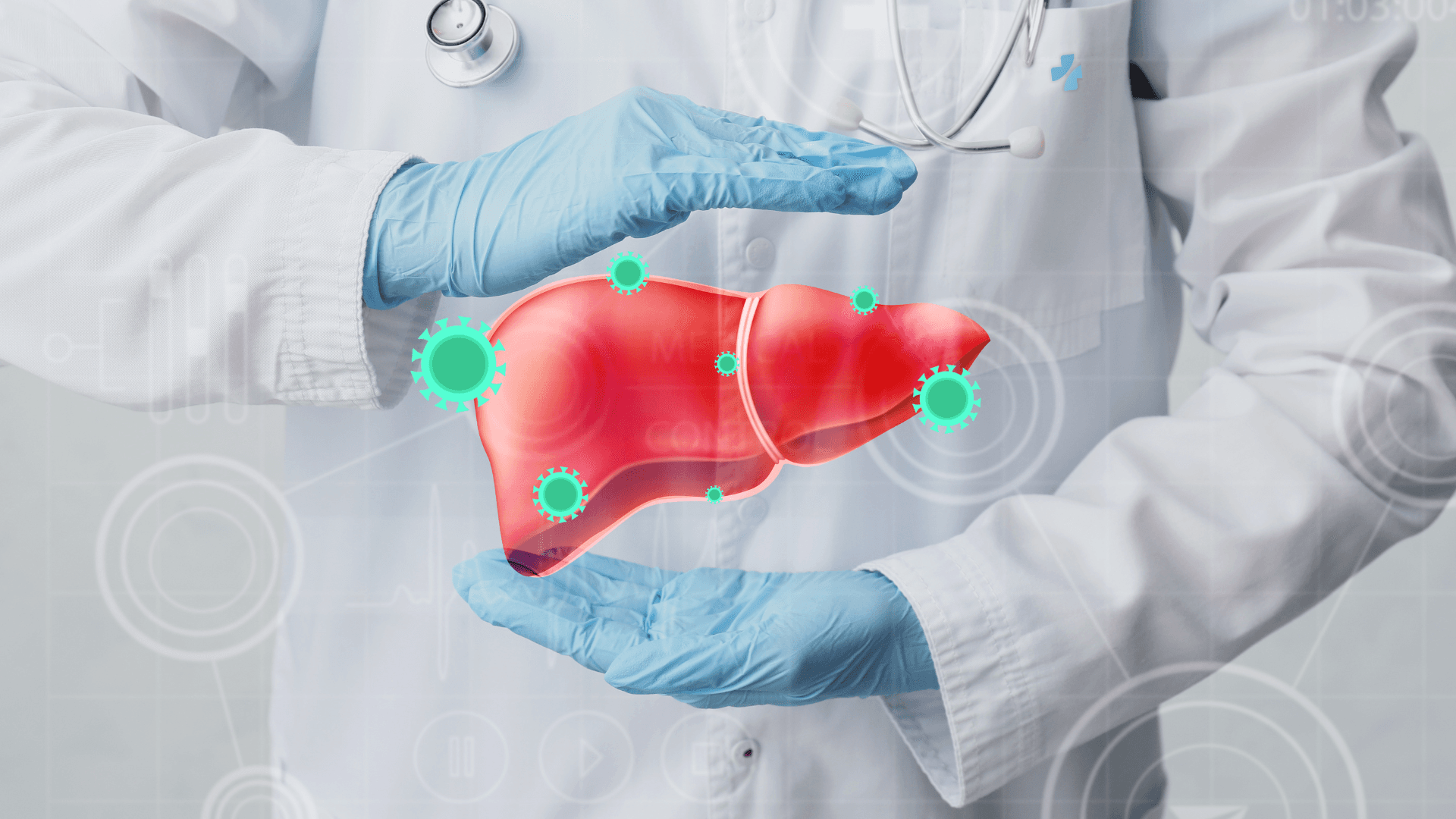
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, commonly caused by viral infections. There are five main types of hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. Each type has unique characteristics, transmission methods, and health implications.
- Hepatitis A and E: These types are usually transmitted through ingesting contaminated food or water. They are often linked to poor sanitation and are more common in developing countries.
- Hepatitis B, C, and D: These are primarily spread through contact with infected body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal fluids. Common transmission routes include unsafe injections, blood transfusions, and unprotected sexual contact.
Symptoms and Impact
The symptoms of hepatitis can range from mild to severe. Common signs include fatigue, flu-like symptoms, dark urine, pale stool, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). However, many people, especially those with hepatitis C, might not exhibit symptoms for years, which makes early detection challenging.
Chronic hepatitis B and C are particularly concerning. These infections can persist for decades and lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Globally, approximately 257 million people live with chronic hepatitis B, and 71 million with chronic hepatitis C.
Prevention and Vaccination
Prevention is crucial in the fight against hepatitis. Vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B, and they have proven to be highly effective. The hepatitis B vaccine is typically administered to infants at birth and provides more than 95% protection against the infection.
While there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, ongoing research offers hope for future prevention methods. Until then, preventing transmission through safe practices—such as using clean needles, screening blood transfusions, and practicing safe sex—is essential.
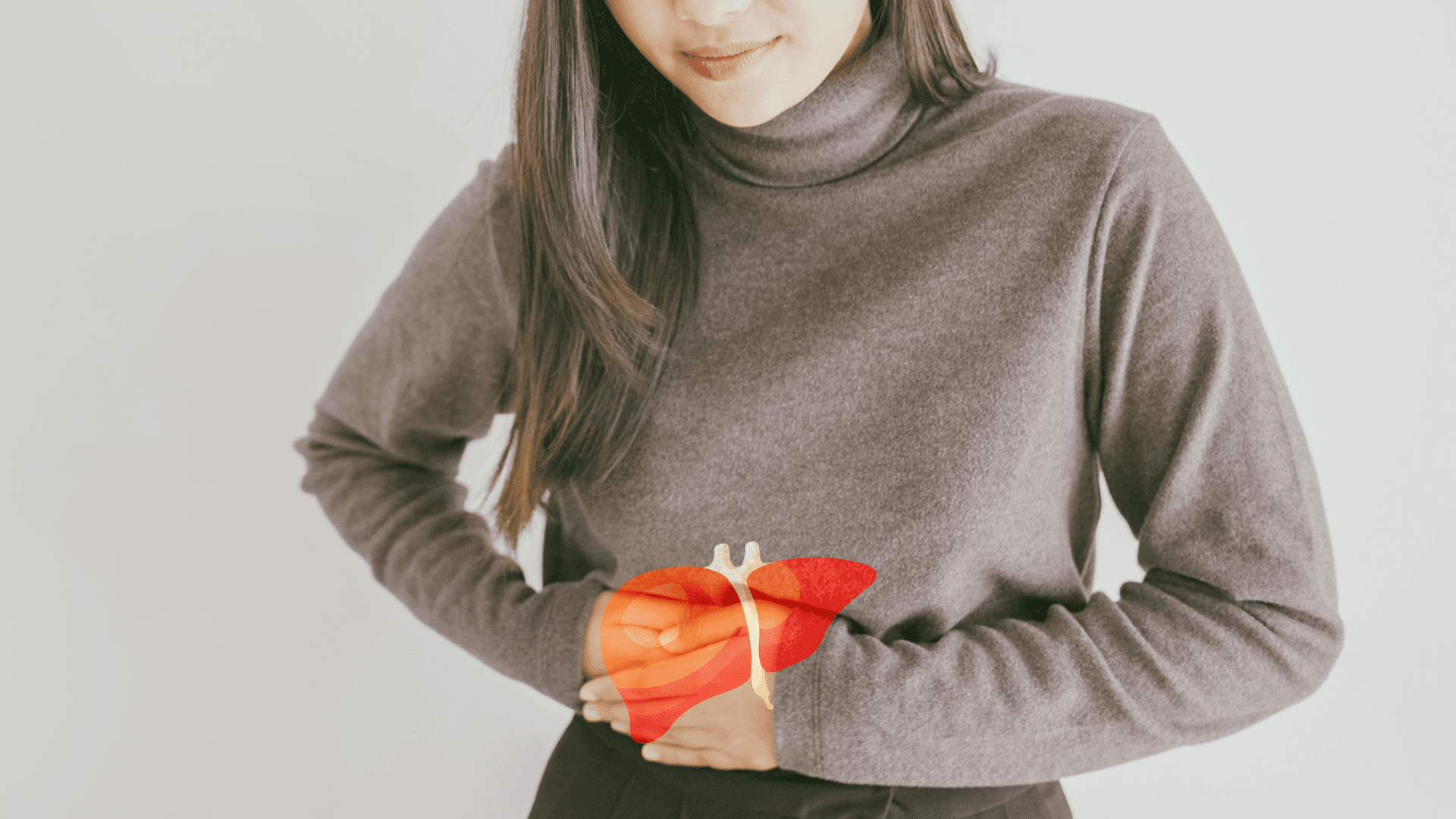

Treatment and Hope
Acute hepatitis infections often resolve on their own, but chronic infections require medical intervention. Antiviral medications can manage chronic hepatitis B, reducing the risk of liver damage and other complications. Exciting advancements have been made in treating hepatitis C, with direct-acting antiviral drugs now able to cure the infection in most cases.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to combating hepatitis. Regular screening, especially for those at higher risk, can lead to early intervention and better health outcomes.
Getting Involved
World Hepatitis Day 2024 calls for a unified effort to eliminate hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030. Here’s how you can contribute:
- Raise Awareness: Share information about hepatitis with your community. Use social media, organize local events, or participate in awareness campaigns.
- Get Tested: Knowing your hepatitis status is crucial. Encourage others to get tested, especially those in high-risk groups.
- Support Vaccination: Promote hepatitis A and B vaccinations. Ensure that those around you, especially children, are vaccinated.
- Advocate for Funding: Support organizations and initiatives that are working to provide better prevention, testing, and treatment options worldwide.
Conclusion
World Hepatitis Day 2024 is a reminder that we all have a role to play in the fight against hepatitis. Through awareness, prevention, and early intervention, we can make significant strides in reducing the global burden of this disease. Let us come together to educate, advocate, and take action towards a future free of hepatitis.