Osteoporosis: Understanding the Silent Bone Thief and How to Detect It
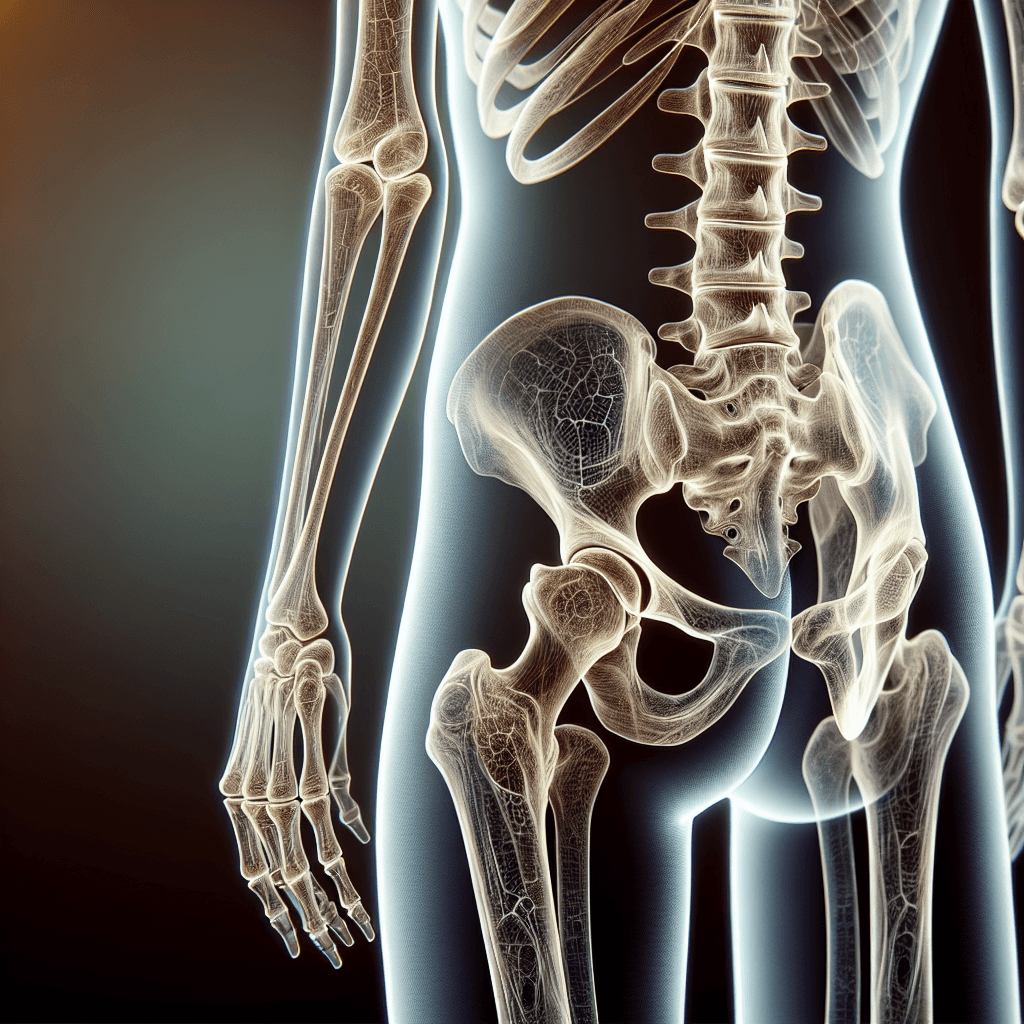
Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more prone to fracture. It is often called the 'silent thief' because bone loss occurs without symptoms. Bones affected by osteoporosis can become so fragile that fractures occur spontaneously or as the result of minor bumps, falls, or normal stresses like bending over or coughing.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including aging, hormonal changes, family history, low body weight, and certain medications. Understanding these can help in early identification and prevention.
Preventive Measures
Prevention strategies include adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, regular weight-bearing exercise, and lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption.
Diagnostic Tests
Early detection of osteoporosis is crucial for effective management. Bone density tests, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), are the gold standard for diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for osteoporosis may include medications that slow bone loss or increase bone formation, as well as lifestyle modifications and fall prevention strategies to reduce the risk of fractures.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with osteoporosis means making adjustments to protect your bones. This includes engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet rich in bone-healthy nutrients, and avoiding activities that may lead to falls.